Pictures from the Computer History Museum
A visual history of computingComputer History Museum | piero scaruffi | A History of Silicon Valley
More pictures: Historical buildings of Silicon Valley | Computer History Museum | Digibarn Computer Museum

Special exhibit of january 2011

Georg von Peuerbach's "Tractatus super propositiones Ptolemaei de sinubus & chordis" (1468), the oldest extant book of mathematical tables

John Napier's "Bones" (1617)

John Napier's "Bones" (1617)

Schickard Calculator (1623)

Pascaline (1642)

Jacquard loom cards, invented by invented by Joseph Marie Jacquard in 1801, the predecessors of computer punched cards

Jacquard loom cards, invented by invented by Joseph Marie Jacquard in 1801, the predecessors of computer punched cards

Jacquard loom cards, invented by invented by Joseph Marie Jacquard in 1801, the predecessors of computer punched cards

Babbage Differential Engine 1 (1833)

Babbage Differential Engine 1 (1833)

Elizur Wright Arithmeter, Joseph Fowle (1869)

Lord Calculator, Elliott Brothers (1880)

Hollerith Electric Tabulating Machine (1890)
 Hollerith Electric Tabulating Machine (1890)
Hollerith Electric Tabulating Machine (1890)

Hollerith's Pantograph Card Punch (1900)

Paul Otlet's library of world knowledge Mundaneum (1910)

Burroughs Adding Machine (1912)

Felt & Tarrant's Comptometer (1890), the first keyboard adding machine invented in 1887 by Dorr Felt

IBM advert of 1933

IBM advert of 1933

IBM advert of 1933

IBM advert of 1933

John Turing, the mathematician who conceived the Universal Turing Machine (1937)

George Stibitz's Complex Number Calculator (1940), a relay-based computer for Bell Labs

Konrad Zuse' Z3 (1941), the first hardware implementation of the universal Turing machine

Atanasoff-Berry Computer (ABC) at Iowa State Univ (1942) designed by John Atanasoff, consider the first real computer

Atanasoff-Berry Computer (ABC) at Iowa State Univ (1942) designed by John Atanasoff, consider the first real computer

Atanasoff-Berry Computer (ABC) at Iowa State Univ (1942) designed by John Atanasoff, consider the first real computer

John Atanasoff

Colossus Mark I (1943), designed by Tommy Flowers, the first programmable digital electronic computer

Colossus

Colossus

Colossus

Colossus

Conrad Aiken's Harvard Mark I (1944)

The ENIAC (1946), the first commercial computer

ENIAC's Portable Function Table

ENIAC

ENIAC

ENIAC

ENIAC

Invetors of the transistor (1948) at Bell Labs: John Bardeen, William Shockley, and Walter Brattain

William Shockley

The first transistor

Turing and his paper on machine intelligence (1949)

IBM's Type 26 card punch (1949)

IBM's Type 26 card punch (1949)
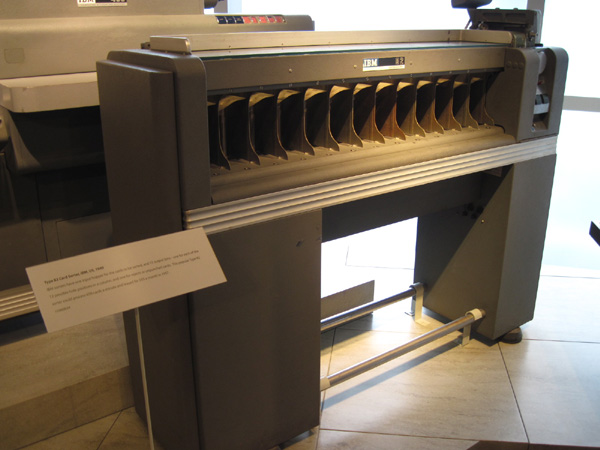

IBM's card sorter (1949)

John Von Neumann with Princeton's IAS stored-program computer (1951)

John Von Neumann and Robert Oppenheimer in front of the IAS (1952)

MIT's Whirlwind computer (1951)

MIT's Whirlwind computer (1951)

MIT's Whirlwind computer (1951)
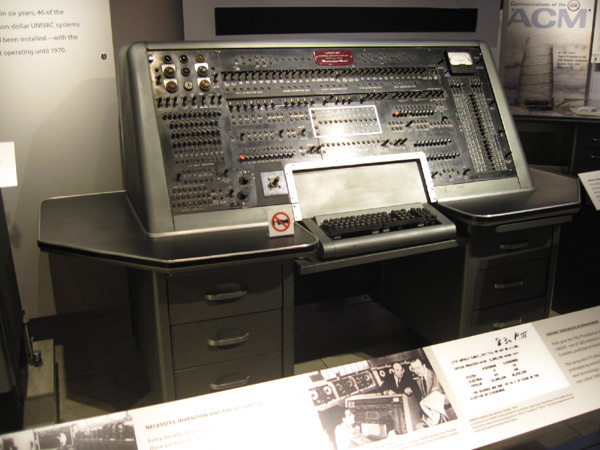

Univac I (1951)

Univac I (1951)

Univac I (1951)

Univac I (1951)

Univac I (1951)

IBM's electromechanical data processor Type 403 (1953)

Rand Corp's Johnniac (1954), based on the IAS

Rand Corp's Johnniac (1954), based on the IAS

Rand Corp's Johnniac (1954), based on the IAS

US Government's SAGE project (1954)

SAGE

SAGE

SAGE

SAGE

SAGE

SAGE

SAGE

SAGE

SAGE

SAGE

SAGE

SAGE

SAGE

SAGE

SAGE

Regency TR-1 transistor radio (1954), the first transistor-based device for the mass market

IBM's RAMAC (1956), the first computer to use magnetic-disk storage

The RAMAC

IBM's RAMAC disc

Magnetic core memory board (1956)

Harry Huskey's CDC Bendix G-15 (1956)

Harry Huskey's CDC Bendix G-15 (1956)

John McCarthy's at Dartmouth (1956)

Founding fathers of Artificial Intelligence (1956)

General Problem Solver's team (1957)

Fairchild founders (1957)

Fairchild founders

A Fairchild integrated circuit

Jean Horni of Fairchild

Robert Noyce of Fairchild

Kilby's integrated circuit (1958)

Kilby's integrated circuit (1958)

Digital Equipment's PDP-1 (1960)

Digital Equipment's PDP-1 (1960)

Digital Equipment's PDP-1 (1960)

Digital Equipment's PDP-1 (1960)

Stanford Cart (1960)

Stanford Cart (1960)

Stanford Cart (1960)

Stanford Cart (1960)

Univac's Livermore Advanced Research Computer (LARC) for the Livermore Lab, a "supercomputer" to design atomic bombs (1960)

IBM's Stretch 7030 (1961)

IBM's Stretch 7030 (1961)

IBM's Stretch 7030 (1961)

Wes Clark's LINC (1962)

Wes Clark's LINC (1962)

LINC

LINC

Apollo Mission's computer logic (1962), one of the biggest users of integrated circuits

Douglas Engelbart, who invented the mouse (1963) at the Stanford Research Institute

IBM /360 (1964)

IBM /360 (1964)

IBM /360 (1964)

IBM /360 (1964)

IBM /360 (1964)

IBM/360

IBM/360

IBM/360

IBM/360

IBM/360

Seymour Cray's CDC 6600 supercomputer (1964)

Seymour Cray's CDC 6600 supercomputer (1964)

CDC 6600

CDC 6600

Moore's Law (1965)

Gordon Moore

Olivetti P101 (1965)
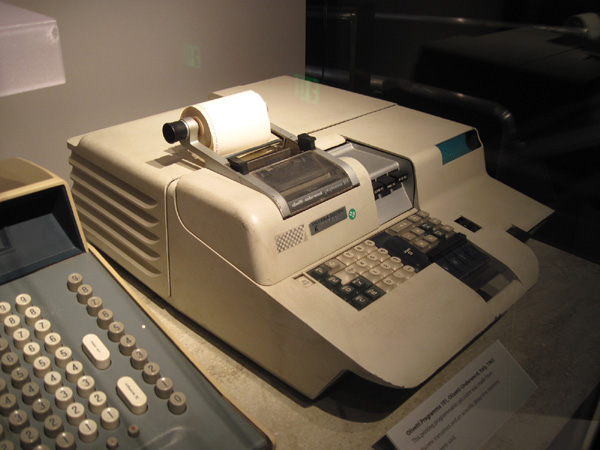

Olivetti P101 (1965)

Olivetti P101 (1965)

Olivetti P101 (1965)

Project Genie at UC Berkeley (1965)

Digital Equipment's PDP-8 (1965)

Digital Equipment's PDP-8 (1965)

Digital Equipment's PDP-8 (1965)

Dendral's team (1965)

Michael Noll 's "Vertical Horizontal" (1965)

Computer artist Howard Wise

Ivan Sutherland's head display (1968)

Ralph Baer's Brown Box (1968), the first home gaming console

Fairchild's 256-bit SRAM (1969)

Digital's PDP-11 (1970)

Digital's PDP-11 (1970)

Tymshare's machine room (1970), full of SDS 940 computers

Intel 1103: 1024-bit DRAM (1970)

The 8" floppy disk (1971)

Ken Thompson and Dennis Ritchie (1972), inventors of Unix

Unix plate

John Blankenbaker's Kenbak-1 (1971), the first commercially available personal computer (but it was not using a microprocessor)

The Kenbak-1

The Kenbak-1

Intel 4004 microprocessor (1971)

Intel 4004

Ted Hoff

Federico Faggin

Early pocket scientific calculators: Bowmar MX55 (1971), HP-35 (1972), Texas Instruments SR-50 (1974), HP-65 (1974)

Ralph Baer's Magnavox Odyssey (1972)

Computer artist Harold Cohen, inventor of AARON (1973), the artist machine

AARON in 1995

Xerox Alto (1973)

Xerox Alto's team

Mouse of the Alto

Robert Metcalfe and David Boggs, inventors of the Ethernet (1973)

Wang 2200 (1973)

Wang 2200

Motorola 68000 (1974)

The Homebrew Club (1974)

Ed Roberts' Altair 8800 (1975)

Ed Roberts' Altair 8800 (1975)

Ed Roberts' Altair 8800 (1975)

Ed Roberts of Altair

Bill Gates and Paul Allen, founders of Microsoft (1975)

IMSAI 8080 (1975)

IMSAI 8080 (1975)

IMSAI 8080 (1975)

Illiac IV parallel computer (1975)

Illiac IV parallel computer (1975)

Cray 1A supercomputer (1976)

Cray 1

The 5.25" floppy disk (1976)

Fairchild's Channel F Video Entertainment System (1976)

Atari Pong console (1976)

Apple I (1976)

Apple II (1977)

Larry Ellison, founder of Oracle (1977)

The founders of Oracle (1977)

Commodore PET (1977)

Commodore PET

Commodore PET (1977)

Commodore PET

Tandy TRS-80 (1977)

Tandy TRS-80 (1977)

Sol (1978)

Atari 2600 (1978)
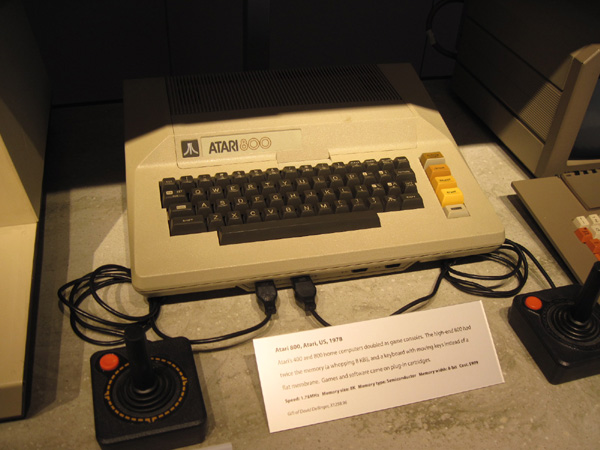

Atari 800 (1978)
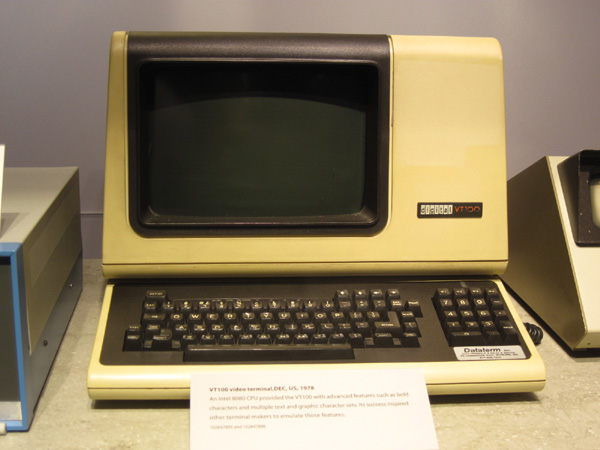

Digital's VT100 terminal (1978)

Steve Jobs and Apple II (1979)

Shakey, SRI's robot (1979)

Shakey

Shakey

Shakey at work

Shakey
Shakey

Shakey

Shakey

Shakey's team

Hubot (1981)

Osborne 1 (1981)

Osborne 1

IBM PC (1981)

Grid Compass (1982)

SUN 1 (1982)

Compaq Portable (1983)

Nintendo Entertainment System (1983), the console that introduced the game SuperMario

Apollo Domain (1984)

Apple Lisa II (1983)

Apple Macintosh (1984)

Macintosh and Lisa II

Macintosh and Lisa II

Psion (1984), the first personal digital assistant, the first hand-held computer

Omnibot 2000 (1984)

Omnibot 2000

Omnibot 2000

Robots of the 1980s

Officer Mac (1985)

Officer Mac (1985)

Sentry (1986)

Hero Jr

Sega Master System Power Base gaming console (1986)

Cisco's Advanced Gateway Server (1986)

Daniel Hillis' Connection Machine (1986)

Daniel Hillis

Connection Machine in operation

Grid Tablet (1989)

Marc Andreessen, who developed Mosaic (1993), the first browser for the World Wide Web

Palm Pilot (1996)

Palm Pilot's team

Palm Pilot's Jeff Hawkins and Donna Dubinsky

Blackberry 5810 (2002)
More pictures: Historical buildings of Silicon Valley | Computer History Museum | Digibarn Computer Museum